Difference between revisions of "Pumping Systems"
(Created page with "The three types of pump systems: positive displacement, momentum transfer, and entrapment. Positive displacement: Uses a mechanism to repeatedly expand a cavity, allow gases ...") |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Rotary: [[File:rotarypump.jpg]] | Rotary: [[File:rotarypump.jpg]] | ||
| − | Screw: [[File:screwpump.jpg]] | + | Screw: [[File:screwpump.jpg| 500px]] |
Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber. Ex: Diffusion and turbo molecular | Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber. Ex: Diffusion and turbo molecular | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Diffusion: [[File:diffusionpump.png]] | Diffusion: [[File:diffusionpump.png]] | ||
| − | Turbo molecular: [[File:Cut_through_turbomolecular_pump.jpg]] | + | Turbo molecular: [[File:Cut_through_turbomolecular_pump.jpg|300px]] |
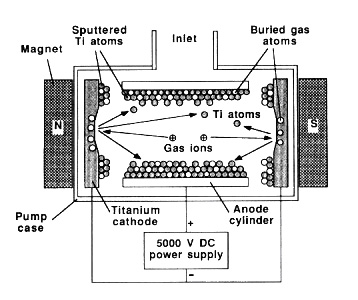
Entrapment: capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state. Ex: Ion and sorption pumps | Entrapment: capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state. Ex: Ion and sorption pumps | ||
Ion: [[File:ionpump.jpg]] | Ion: [[File:ionpump.jpg]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:48, 15 June 2014
The three types of pump systems: positive displacement, momentum transfer, and entrapment.
Positive displacement: Uses a mechanism to repeatedly expand a cavity, allow gases to flow in from the chamber, seal off the cavity, and exhaust it to the atmosphere. Ex: rotary and screw pumps
Momentum transfer: Uses high speed jets of dense fluid or high speed rotating blades to knock gas molecules out of the chamber. Ex: Diffusion and turbo molecular
Entrapment: capture gases in a solid or adsorbed state. Ex: Ion and sorption pumps