Difference between revisions of "Astronomical Spectroscopy"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The overall goal of the Astronomical Spectroscopy Project is to be able to collect and reduce data gathered from astronomical objects. | + | The overall goal of the Astronomical Spectroscopy Project is to be able to collect and reduce data gathered from astronomical objects. Before spectra can be collected, the system needs to be prepared. This preparation involves aligning the telescope-fiber system and calculating the efficiency of the ratio to determine that the project is feasible with the current setup. |
| − | + | The current setup for the project involves a Celestron CPC 800 GPS (XLT) telescope and a fiber-fed Ocean Optics USB2000+ spectrometer. | |
[[File:TelescopeSystem.png]] [[File:TAdapter.png]] | [[File:TelescopeSystem.png]] [[File:TAdapter.png]] | ||
| − | Efficiency of the system is calculated using a lab table procedure. | + | Efficiency of the more basic system is calculated using a lab table procedure. An efficiency of the entire telescope system can be used in comparison to create an efficiency ratio of the system. |
[[File:LabTableSetup.png]] | [[File:LabTableSetup.png]] | ||
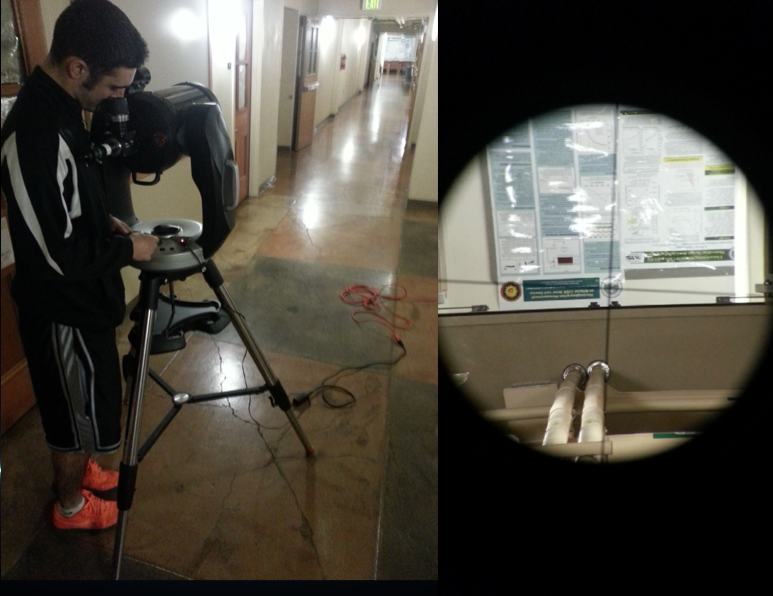
| − | All of the telescope alignment takes place at long distances, like the Willamette Basement Hallways. | + | All of the telescope alignment takes place at long distances greater than the focal distance of the telescope, like the Willamette Basement Hallways. Here, the finderscope is being aligned to the eyepiece. |
[[File:AligningTelescope.png]] | [[File:AligningTelescope.png]] | ||
| − | The fiber alignment process is done in large areas as well, including the Willamette Basement Hallways, but dark rooms like Willamette 100 have given the best results. | + | The fiber alignment process, which involves aligning the fiber to the eyepiece, is the most difficult part of the preparation. This is done in large areas as well, including the Willamette Basement Hallways, but dark rooms like Willamette 100 have given the best results. |
[[File:AligningFiber.png]] | [[File:AligningFiber.png]] | ||
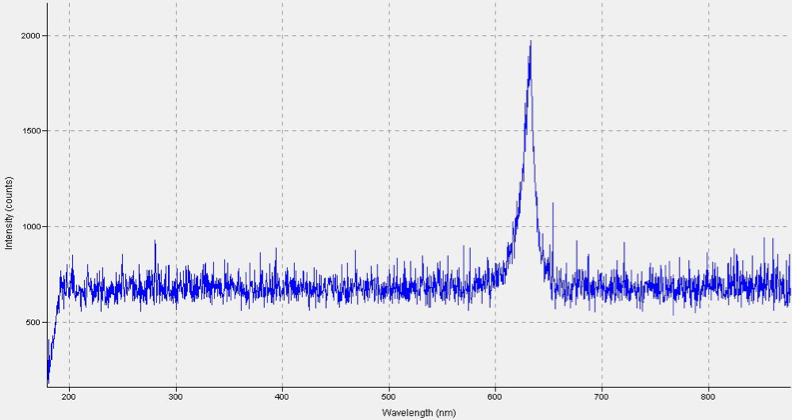
| − | Data is collected during the alignment process to track max number of counts. | + | Data is collected during the alignment process to track the max number of counts read by the spectrometer. |
[[File:AlignmentData.png]] | [[File:AlignmentData.png]] | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 7 December 2013
The overall goal of the Astronomical Spectroscopy Project is to be able to collect and reduce data gathered from astronomical objects. Before spectra can be collected, the system needs to be prepared. This preparation involves aligning the telescope-fiber system and calculating the efficiency of the ratio to determine that the project is feasible with the current setup.
The current setup for the project involves a Celestron CPC 800 GPS (XLT) telescope and a fiber-fed Ocean Optics USB2000+ spectrometer.
Efficiency of the more basic system is calculated using a lab table procedure. An efficiency of the entire telescope system can be used in comparison to create an efficiency ratio of the system.
All of the telescope alignment takes place at long distances greater than the focal distance of the telescope, like the Willamette Basement Hallways. Here, the finderscope is being aligned to the eyepiece.
The fiber alignment process, which involves aligning the fiber to the eyepiece, is the most difficult part of the preparation. This is done in large areas as well, including the Willamette Basement Hallways, but dark rooms like Willamette 100 have given the best results.
Data is collected during the alignment process to track the max number of counts read by the spectrometer.
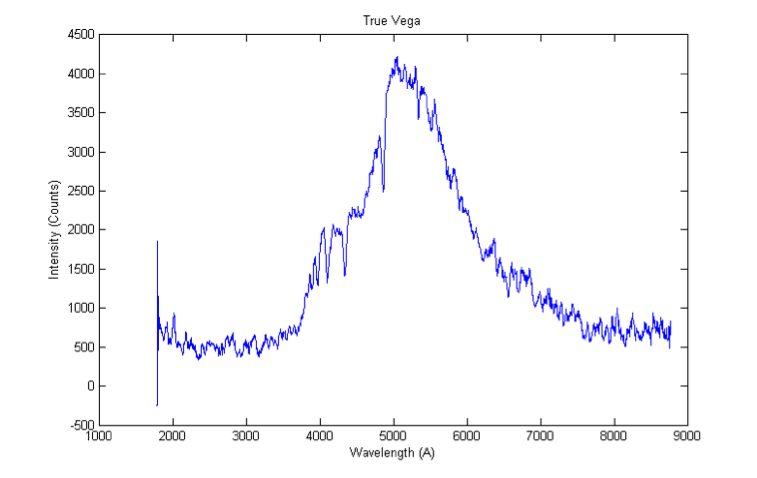
The furthest progress that has been made on the project is successfully getting a spectra of Vega using the SpectraSuite software. However, the integration time used to get the spectra was 60 seconds with a scans to average of 10, and box car smoothing of 10.
Presentations:
Links: